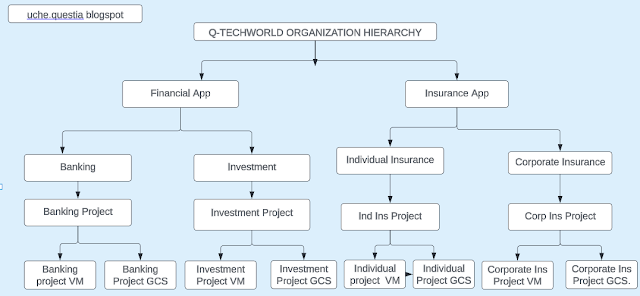
Today, you will attach a persistent disk to an existing VM or attaching a new disk without stoping the VM.
STEP 1:
Create a folder in your local "Google-Cloud-Platform"
STEP 2:
Within step 1 folder, create a folder "Compute"
STEP 3:
Within step 2 folder, Create two folders "Compute-Engine and APP-Engine".
STEP 4:
Create a file "jjtechflix-app-deploy.sh"within compute-engine. Any script that has .sh is a shell script and can only run in a linux machine.
STEP 5:
Paste script within the file and technically you should have 11 lines of codes and save.
#! /bin/bash
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt -y install apache2
sudo systemctl start apache2
sudo systemctl enable apache2
sudo apt install wget -y
sudo wget https://github.com/awanmbandi/google-cloud-projects/raw/jjtech-flix-app/jjtech-streaming-application-v1.zip
sudo apt install unzip -y
sudo unzip jjtech-streaming-application-v1.zip
sudo rm -f /var/www/html/index.html
sudo cp -rf jjtech-streaming-application-v1/* /var/www/html/
STEP 6:
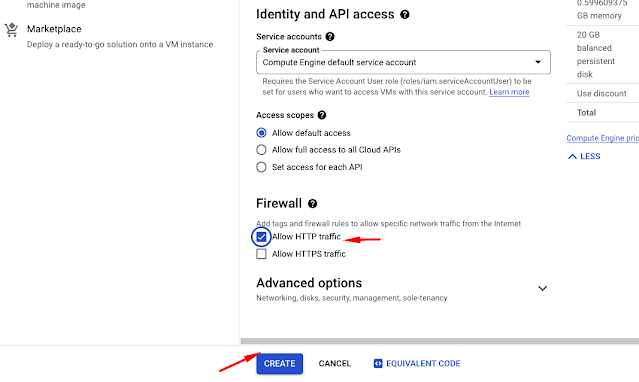
Create a VM, allow HTTP traffic, expand advance option and expand management, you'll see automation start script and ensure that you pass the data at the level and create.
#! /bin/bash - Allow you to run operations inside linux.
STEP 7:
Copy your external IP address and run on your browser, click on the disk. You should see the application you deployed. This is not a secured site.
STEP 8:You're creating a second disk to attach to an existing VM. Click on disk and it tells you exactly what VM is associated with the disk. You create a disk. The second disk will not be refer to as a boot disk because it has no image, OS.
STEP 9:
Go back to VM , click the name you created and click on edit. Your interest is within edit. You can start changing things within the panels, its either you're changing or adding.
STEP 10:
Search for storage, you'll see the boot disk which you configured. Select "keep disk". This means that, even though you delete the VM, the disk will not be deleted. Click on add new disk and save.
STEP 11: You created an additional disk that has no image. You will create a custom image from this disk and attached an instance.
STEP 12:
You're preparing for disaster recovery strategies on the application. The application is running within the boot disk that is powering the VM. We need to focus on the actual boot disk. In order to achieve this, you create a custom image from the existing VM and you'll still able to recovery and access it.
Click on the instance name and create machine image.
You select the option "regional" to save cost. The multi will incur cost. And create.
By default when you create a custom image it will automatically capture the additional disk that you initially create including the boot disk. Within the created custom image you can create an instance Create instance from the machine image.
change the name of your "vm" and save.
STEP 14:
Snap shot : You will take back up of your persistent disk.
Go to disk and click your VM you created and create snapshot and create.
You can also filter based on labels.
STEP 15:
You're trying to automate snapshot for an application back up. To achieve this, you click on snapshot panel and "create snap shot schedule". Your persistent disk( VM) should be in the same region where the snapshot is taken.
You take snap shot when the application traffic is at its lowest. You have to identify your peak period of request from users. for example, 1am -2am. Once this snap shot is created, by default all the snap shot in that particular region will be taken.
STEP 15:
You've successfully deployed a persistent disk, attached an additional disk and provisioned an image which you then created a custom image. We configured with a snapshot for back-up.
Happy Learning!!😊